the acceleration produced by a net force on an object is|Newton's Second Law Of Motion : Cebu When an object is dropped, it accelerates toward the center of Earth. Newton’s second law states that a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration. If air resistance is negligible, the net . We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
the acceleration produced by a net force on an object is,The acceleration produced by a net force on an object (Newton's 2nd Law) is (a) in the same direction as the net force (b) directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force (c) inversely proportional to the mass of the object (d) all the above (e) none
When an object is dropped, it accelerates toward the center of Earth. Newton’s second law states that a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration. If air resistance is negligible, the net . Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables – the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. The . Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass. Acceleration of an object depends on two things, force and mass. This shows that the bowling experiences a much .When there is a net force on an object, the object will change speed in the direction of the net force. The object’s acceleration tells us how much it speeds up or slows down. .Balanced forces can cause the net force of an object to be zero. Multiple forces can act on an object. If the forces are balanced, the net force is zero and the object’s acceleration is also zero.Newton's Second Law of Motion: All the net forces on one object cause it to accelerate if the net force is other than zero.
Newton’s second law states that the net external force acting on an object is responsible for the acceleration of the object. If air resistance is negligible, the net external force on a .Newton’s first law says that a net external force causes a change in motion; thus, we see that a net external force causes nonzero acceleration. We defined external force in .
the acceleration produced by a net force on an object isThe unbalanced force on the object a. is 3.0 N. b. is 0 N. c. is 5 N. d. is 6 N. e. cannot be determined from given information. . The acceleration produced by an unbalanced force acting on an object is a. inversely proportional to the mass of the object. b. . When a net force on a moving object increases, the object will a. maintain the .
Newton’s second law of motion. Newton’s second law says that the acceleration and net external force are directly proportional, and there is an inversely proportional relationship between acceleration and mass. .The acceleration produced by a certain force depends on the mass of the object. The acceleration of an object with twice the mass of the standard mass under the influence of a certain force is half that of the . Inversely proportional to the object's mass and directly proportional to the amount of the net force acting in the same direction.. What is Acceleration? Acceleration is the rate of variation in a moving object's speed and direction over time.A straight-ahead point or objects is said to be accelerating or receding when it does so.Travelling on a .The Unit of Force is the Newton. Mass. The kilogram (kg) is the unit of mass in physics; This is a measure of the matter in an object; Acceleration. Meters per second squared (m/s 2) is the unit of acceleration; This is a measure of how much faster an object will move every second in a direction
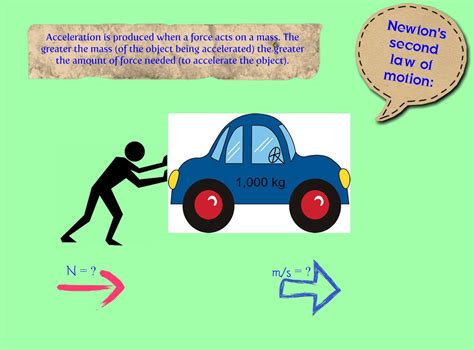
Newton’s 2nd Law relates an object’s mass, the net force on it, and its acceleration: Therefore, we can find the force as follows: Fnet = ma. Substituting the values, we get. 1000 kg × 4 m/s 2 = 4000 N. Therefore, the horizontal net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 4 m/s -2 is 4000 N. Q.13. Assertion : When astronauts throw something in space, that object would continue moving in the same direction and with the same speed. Reason : The acceleration of an object produced by a net applied force is directly related to the magnitude of the force, and inversely related to the mass of the object.Newton's Second Law Of MotionNeglecting friction, to equally accelerate a 10-kilogram brick, one would have to push a. with 100 times as much force b. with 10 times as much force. c. with just as much force. d. with io the amount of force. e. none of the above A rock is thrown vertically into the air. At the very top of its trajectory the net force on it is a. its weight .
the acceleration produced by a net force on an object is Newton's Second Law Of MotionNeglecting friction, to equally accelerate a 10-kilogram brick, one would have to push a. with 100 times as much force b. with 10 times as much force. c. with just as much force. d. with io the amount of force. e. none of the above A rock is thrown vertically into the air. At the very top of its trajectory the net force on it is a. its weight .Newton’s Second Law of Motion. The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and is inversely proportion to its mass. In equation form, Newton’s second law is. a = F net m, (15.3.3) (15.3.3) a → = F → n e t m, where a a → is the acceleration, F net F . An object in motion will stay in motion, traveling in a straight line, forever, until something pushes or pulls on it. Now, we will discuss the second law of motion, which states that: ” The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force .Finding Acceleration from Net Force. If we know the net force and want to find the acceleration, we can solve Newton's Second Law for the acceleration: (2) Now we see that larger net forces create larger accelerations and larger masses reduce the size of the acceleration. In fact, an object’s mass is a direct measure of an objects resistance .In other words, the larger the mass (the inertia), the smaller the acceleration produced by a given force. As illustrated in Figure 5.11, the same net external force applied to a basketball produces a much smaller acceleration when it is applied to an SUV. The proportionality is written asNewton's second law states that for a particular force, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This can be expressed in the form of an equation: In the MKS system of units, the unit of force is the Newton (N). In terms of kilograms, meters, and seconds, 1 N = 1 kg m .

Newton’s second law states that a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration. If air resistance is negligible, the net force . One way to do this is to exert a known force on an astronaut and measure the acceleration produced. Suppose a net external force of 50.0 N is exerted and the astronaut’s acceleration is measured to .Newton’s second law states that a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration. If air resistance is negligible, the net force . One way to do this is to exert a known force on an astronaut and measure the acceleration produced. Suppose a net external force of 50.0 N is exerted and the astronaut’s acceleration is measured to .
Newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. Often expressed as the equation a = Fnet/m (or rearranged to Fnet=m*a), the equation is probably the most important equation in all of Mechanics. It is used to predict how an object will accelerated (magnitude and direction) in the presence of an .Calculate the acceleration produced by a force of 20 N on an object of mass 2 kg. View Solution. Q 4. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by a 15 kg mass on a 25 kg mass separated by a distance of 25 cm. What is the acceleration produced in each mass? [3 marks] An object in motion does not have to slow down ,unless it is acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion can stay in motion, as long it is being acted on either by a .
the acceleration produced by a net force on an object is|Newton's Second Law Of Motion
PH0 · Physics Test 3 Multiple Choice Flashcards
PH1 · Newton’s Second Law: Net Force Causes Acceleration
PH2 · Newton's second law review (article)
PH3 · Newton's second law of motion (video)
PH4 · Newton's Second Law of Motion
PH5 · Newton's Second Law Of Motion
PH6 · Forces and acceleration (article)
PH7 · 5.3 Newton's Second Law
PH8 · 4.3 Newton's Second Law of Motion
PH9 · 2.4: Newton's Second Law of Motion